Terror 26 Methylation
It is the 24 of April 2018.
Previous work with fruit flies had suggested that kinship does indeed change fertility in these insects and that the change is so rapid and cyclic that it cannot be due to DNA mutations but must be brought about by an epigenetic mechanism. There are a number of epigenetic processes, but the easiest approach seemed to be to exploit the fact that methyl groups on DNA can alter the function of genes.
Accordingly I made a cocktail that was reported by Waterson in Diet-induced hypermethylation at agouti viable yellow is not inherited transgenerationally through the female.
Waterland RA, Travisano M, Tahiliani KG.
FASEB J. 2007 Oct;21(12):3380-5. Epub 2007 Jun 5.
I took 30 grams choline, 30 grams betaine, 30 milligrams folic acid, 3 milligrams vitamin B12, 15 grams l-methionine and 30 grams of zinc made up to 1 liter with water. The pills did not dissolve completely, so there was a lot of mixing to assure a consistent content. I called the full strength 100% and did dilutions from there. I found in a side experiment that the flies could tolerate a 40% dilution, but not much more. Waterson apparently worked up to a level where the methyl receptors were saturated. This in flies might have produced a maximum fertility, but that would have been hard to interpret. So I did a control baseline, during which the flies underwent a complete cycle of damped oscillation and then gave them a 40% dilution. Daily counts were made in two windows of the cage and then added together every 2 weeks.
The schedule was this:
Table 1
Dose |
Begin |
End |
Baseline |
July 11, 2010 |
December 8, 2012 |
40 % |
December 9, 2012 |
January 5, 2013 |
30 % |
January 6, 2013 |
April 29, 2013 |
20 % |
April 30, 2013 |
July 23, 2013 |
16 % |
July 24, 2013 |
November 13, 2013 |
13 % |
November 14, 2013 |
March 1, 2014 |
11 % |
March 2, 2014 |
June 23, 2014 |
9 % |
June 24, 2014 |
October 3, 2014 |
7.5 % |
October 4, 2014 |
January 6, 2015 |
6 % |
January 7, 2015 |
April 28, 2015 |
5% |
April 29, 2015 |
August 19, 2015 |
4% |
August 20, 2015 |
November 12, 2015 |
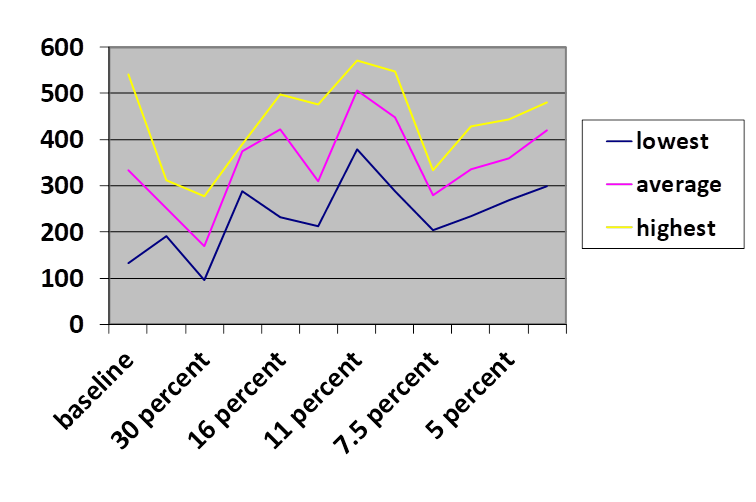
Daily counts in two windows continued and the results pooled over 2 week intervals were examined
The result was
The first observation is that yes, methylation seems to have an effect on fertility. My first impulse was to give 90% confidence intervals, but since there is no certainty that the data are distributed on a normal curve, it seemed clearer at every two-week interval to give an average, a highest value and a lowest value.
There are a number of things that might be going on: 1) there might be a toxic effect from the supplements. 2) There might be a nutritional effect from the supplements. 2) The dilutions are changing. 4) There is definitely an underlying post-zygotic process. However, even using all three I do not see how this complex response could be caused.
Until someone comes up with a better explanation, we are left with the weight of the evidence indicating that there is at least one pre-zygotic mechanism and at least one post-zygotic mechanism and both of these are mediated by a process involving methylation.
YouTube video script directory
Home page.